what type of carbohydrate is lactose Structure and functions of 3 types of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are an essential component of our diet and play a crucial role in providing energy to our bodies. They are one of the three major macronutrients, alongside proteins and fats. In this post, we will explore the structure and functions of three types of carbohydrates: maltose, sucrose, and lactose. Maltose, sucrose, and lactose are all classified as disaccharides, which means they are composed of two sugar units. Maltose is formed by the combination of two glucose molecules, while sucrose is a combination of glucose and fructose. Lactose, on the other hand, consists of glucose and galactose units. Let’s start by looking at the structure and functions of maltose. Maltose is commonly found in cereals, grains, and some root vegetables. Its structure consists of two glucose molecules linked together by a glycosidic bond. This bond can be broken down by enzymes in our bodies into individual glucose molecules, which can then be used as a source of energy. Next, let’s explore sucrose, also known as table sugar. Sucrose is commonly found in sugarcane, sugar beets, and various fruits. Its structure consists of a glucose molecule linked to a fructose molecule via a glycosidic bond. When we consume foods containing sucrose, our bodies break it down into glucose and fructose, which are then absorbed and utilized by our cells for energy production. Lastly, lactose is the primary carbohydrate found in milk and dairy products. Its structure consists of a glucose molecule linked to a galactose molecule via a glycosidic bond. In order to digest lactose properly, our bodies produce an enzyme called lactase. Lactase breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose, which can be absorbed and utilized for energy. Now that we have discussed the structure and functions of these three carbohydrates, let’s understand their importance in our diet. Carbohydrates are a significant source of energy for our bodies, providing approximately 4 calories per gram. They are particularly important for providing fuel to our brain and central nervous system. Additionally, carbohydrates help in the synthesis of other essential molecules in our bodies, such as fatty acids and amino acids. It is important to note that not all carbohydrates are the same in terms of their nutritional value. While complex carbohydrates found in whole grains, vegetables, and legumes are rich in fiber and nutrients, simple carbohydrates like white sugar and refined flour provide mainly empty calories. Therefore, it is recommended to consume carbohydrates from whole food sources and limit the intake of processed and refined carbohydrates. In conclusion, carbohydrates are a vital component of our diet, providing energy and playing various roles in our overall health. Maltose, sucrose, and lactose are three types of carbohydrates with distinct structures and functions. Understanding the importance of carbohydrates and making mindful choices in our diet can contribute to our overall well-being.
If you are looking for What Is Carbohydrate? What Type Of Carbohydrate Is Sucrose, Lactose you’ve came to the right place. We have 5 Images about What Is Carbohydrate? What Type Of Carbohydrate Is Sucrose, Lactose like 6.2: Types of Carbohydrates - Medicine LibreTexts, What Is Carbohydrate? What Type Of Carbohydrate Is Sucrose, Lactose and also Biochemical Properties of Carbohydrates - The Medical Biochemistry Page. Here it is:
What Is Carbohydrate? What Type Of Carbohydrate Is Sucrose, Lactose
 www.paramedicalinfo.comcarbohydrate
www.paramedicalinfo.comcarbohydrate
Biochemical Properties Of Carbohydrates - The Medical Biochemistry Page
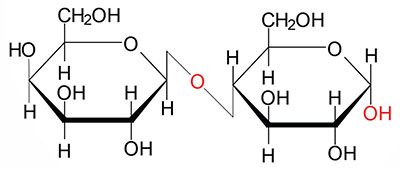 themedicalbiochemistrypage.orglactose carbohydrates biochemistry galactose glucose glycosidic biochemical exclusively mammals consists milk
themedicalbiochemistrypage.orglactose carbohydrates biochemistry galactose glucose glycosidic biochemical exclusively mammals consists milk
Classification Of Carbohydrates With Definition, Types Of Carbohydrates
 byjus.comcarbohydrates classification examples byjus
byjus.comcarbohydrates classification examples byjus
Structure And Functions Of 3 Types Of Carbohydrates - Biology
 biology.reachingfordreams.comdisaccharides lactose carbohydrates biology sucrose structure examples polysaccharide glycosidic types mono sugar bonds table maltose disaccharide two oligosaccharides milk functions
biology.reachingfordreams.comdisaccharides lactose carbohydrates biology sucrose structure examples polysaccharide glycosidic types mono sugar bonds table maltose disaccharide two oligosaccharides milk functions
6.2: Types Of Carbohydrates - Medicine LibreTexts
 med.libretexts.orglactose structure carbohydrates types chemical libretexts molecule medicine haworth
med.libretexts.orglactose structure carbohydrates types chemical libretexts molecule medicine haworth
Disaccharides lactose carbohydrates biology sucrose structure examples polysaccharide glycosidic types mono sugar bonds table maltose disaccharide two oligosaccharides milk functions. 6.2: types of carbohydrates. Classification of carbohydrates with definition, types of carbohydrates